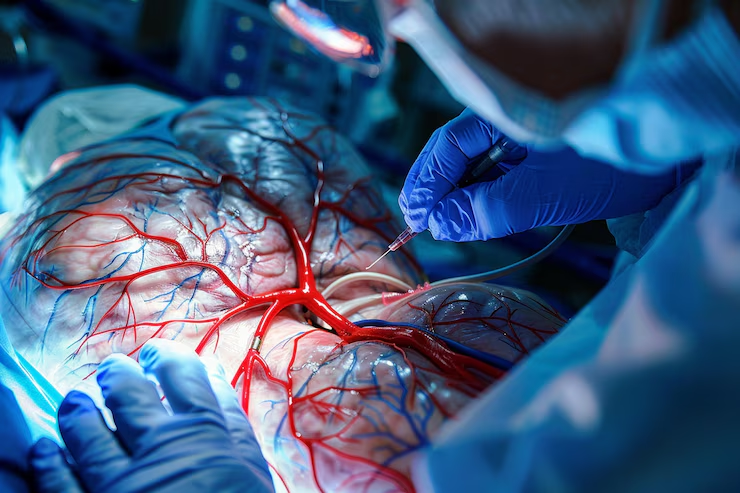
Provides clear, detailed, and precise images of blood vessels
Accurately detects blockages, narrowing (stenosis), aneurysms, and malformations
Allows real-time visualization of blood flow through vessels
Helps locate the exact site and severity of vascular problems
Guides treatment decisions such as angioplasty, stent placement, or surgery
Can combine diagnosis and treatment in one procedure (e.g., angioplasty during angiography)
Minimally invasive compared to open surgery
Usually quick procedure with relatively short recovery time
Can be performed on an outpatient basis
Useful in emergency situations like heart attacks or strokes for rapid diagnosis and intervention
Provides detailed vascular anatomy needed before complex surgeries
Helps monitor disease progression or effectiveness of previous treatments
Can detect abnormalities that might be missed by other imaging techniques
Allows targeted therapy, reducing the need for more invasive interventions
Helps assess collateral circulation and blood flow dynamics
Improves patient outcomes by enabling early and accurate diagnosis